Collaborative Filtering
Before we get started with the actual implementation, let's go through some concepts with building a recommendation engine.
There are essentially 3 types of algorithm that your recommendation engine could use when recommending an item to a user:
1. Demographic Filtering
This type of filtering looks at the general trends and popularity of an item based on users with similar demographics. This means that users with similar demographics are recommended the same items and personalized recommendations are very limited.
2. Content-Based Filtering
The underlying algorithm for this type of filtering looks at the similarity of items based on its metadata. For example, for games, the metadata would be things like platforms, genres, and publisher. Therefore, if a user liked a PC action RPG game that is published by Valve, then most likely he or she would like another game that has similar metadata (i.e., games that are published by Valve and are action RPG PC games). This means that personalized recommendations are now involved, since games that the user liked is used to determine games that the user will probably like too.
The only problem with this type of filtering is the fact that items are recommended in a limited pattern, that is through its metadata.
3. Collaborative Filtering
The final type of filtering can be broken to two types.
- User-based: matches users to items based on other users. Specifically, other users that are determined to be similar to the user by the algorithm. This means given a user and another user that is found to be similar to the user, what the other user liked is recommended to the user.
- Item-based: matches users to items based on items' similarity with items that the user has rated. This means if a user liked item X, and item X is found to be highly similar to item Y, then item Y will be recommended to the user.
The best type of recommendation engine would obviously integrate all 3 types but in this tutorial, we'll focus on the last type: collaborative filtering, since it is arguably the strongest type.
Matrix Factorization
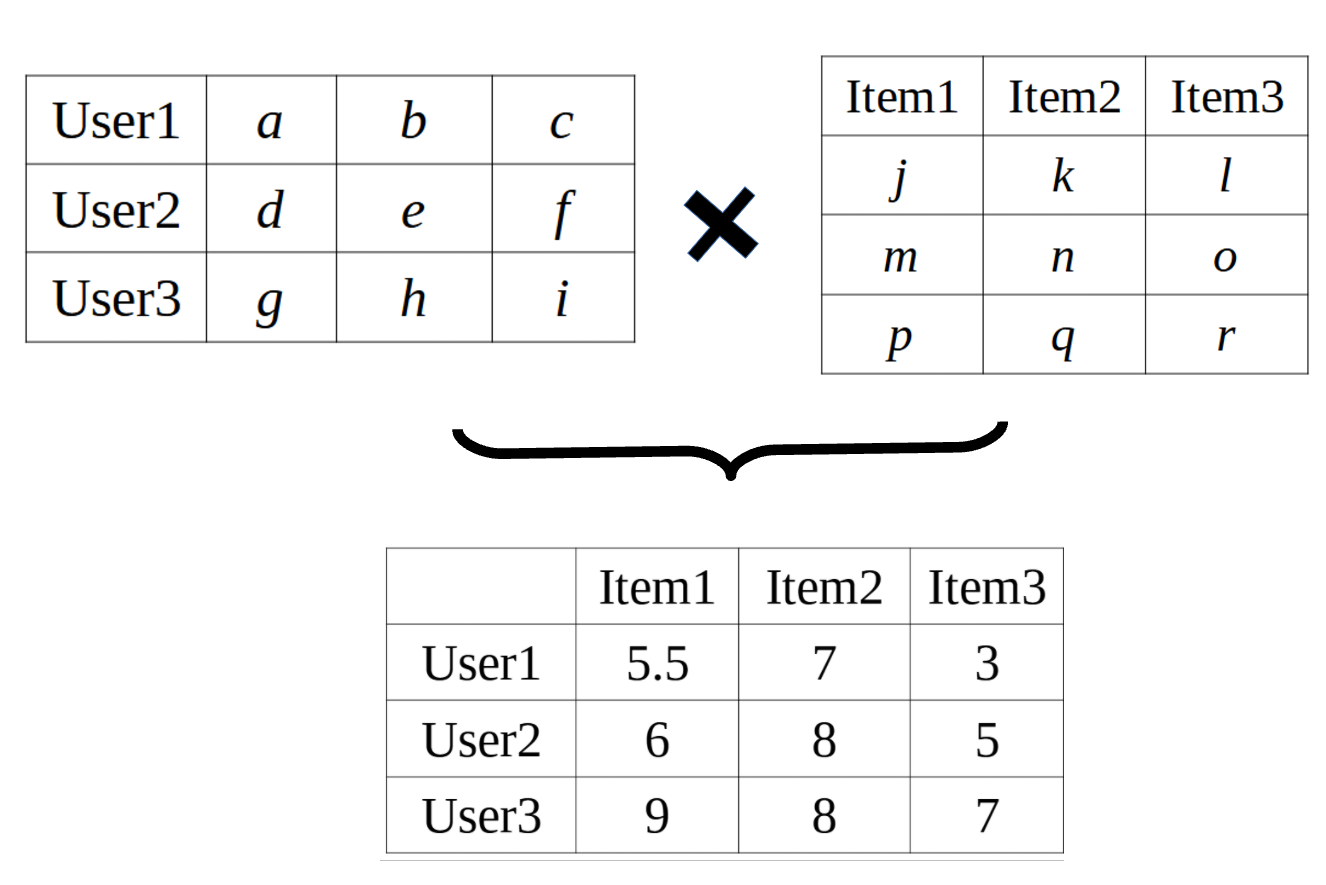
A class of collaborative filtering algorithm that we'll be looking at is called Matrix Factorization. The end goal of matrix factorization is basically to build a matrix of users and items filled with known and predicted ratings.
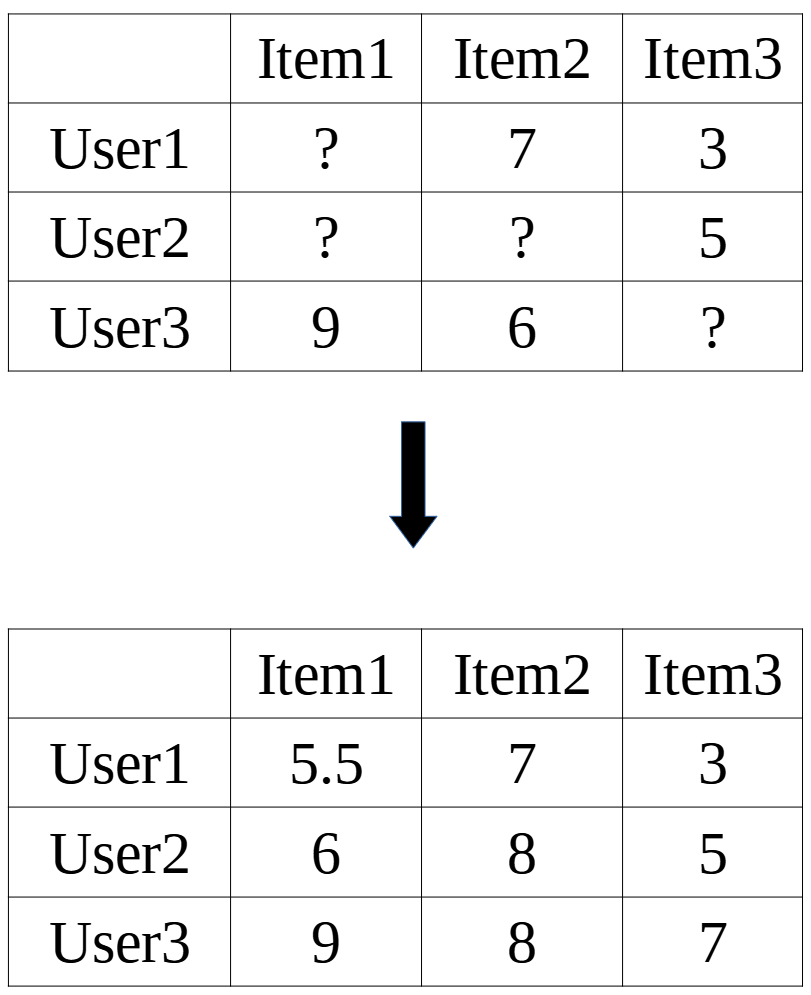
Starting with our original matrix of only known ratings, we want to determine the two factor matrices that would produce our original matrix. These two matrices would in turn represent information of the users, items, and the relationships between them. One being the matrix that quantitatively represent the users (user matrix), where each row of the matrix is a vector of size k that represents a single user, and the other being the item matrix, where each column is a vector of size k that represents a single item.
important
k is called the embedding size and is a hyperparameter that is tuned in the matrix factorization model. A larger embedding size would allow for the model to capture more complex relationships and information, but may lead to overfitting.